The chimney swift is a bird belonging to the swift family Apodidae. A member of the genus Chaetura, it is closely related to both Vaux's swift and Chapman's swift; in the past, the three were sometimes considered to be conspecific. It has no subspecies. The chimney swift is a medium-sized, sooty gray bird with very long, slender wings and very short legs. Like all swifts, it is incapable of perching on flat surfaces, and can only perch on vertical surfaces. Many fly around all day and only come down at night when roosting.
🛡️ Conservation Status
vulnerable
vu
📌 Taxonomy and systematics
When Carl Linnaeus first described the chimney swift in 1758, he named it , believing it to be a swallow. This misconception continued well into the 1800s, with ornithologists calling it "American Swallow" (e.g. Mark Catesby) or "Chimney Swallow" (e.g. John James Audubon). In 1825, James Francis Stephens moved this and other small, short-tailed New World swifts to the genus Chaetura, where it has since remained, although some authorities in the 1800s assigned it to a variety of now obsolete genera. It has no subspecies. The chimney swift's closest relative is Vaux's swift (C. vauxi). Scientists believe that the two species evolved from a common ancestor that was forced to North America's southeastern and southwestern corners by glacial advances. Separated for millennia by vast ice sheets, the survivors evolved into two species which are still separated by a wide gap across the continent's midsection. It is also closely related to the Chapman's swift (C. chapmani); in the past, the three were sometimes treated as a single species.
The chimney swift's genus name, Chaetura, is a combination of two Ancient Greek words: , which means "bristle" or "spine", and , which means "tail". This is an apt description of the bird's tail, as the shafts of all ten tail feathers (rectrices) end in sharp, protruding points. The specific name pelagica is derived from the Greek word pelagikos, which means "of the sea". This is thought to be a reference to its nomadic lifestyle rather than to any reference to the sea, a theory strengthened by the later assignment of the specific name pelasgia (after the nomadic Pelasgi tribe of ancient Greece) to the same species by other ornithologists. Its common name refers to its preferred nesting site and its speedy flight.
📌 Similar species
The chimney swift looks very much like the closely related Vaux's swift, but is slightly larger, with relatively longer wings and tail, slower wingbeats and a greater tendency to soar. It tends to be darker on the breast and rump than the Vaux's swift, though there is some overlap in plumage coloring. It can be as much as 30 percent heavier than Vaux's swift, and its wings, which are proportionately narrower, show a pronounced bulge in the inner secondaries. The chimney swift is smaller, paler and shorter tailed than the black swift. In Central America, it is most similar to Chapman's swift, but it is paler (matte olive rather than glossy black) and has a stronger contrast between its pale throat and the rest of its underparts than does its more uniformly colored relative.
📌 Distribution and habitat
A widespread breeding visitor to much of the eastern half of the United States and the southern reaches of eastern Canada, the chimney swift migrates to South America for the winter. It is a rare summer visitor to the western U.S, and has been recorded as a vagrant in Anguilla, Barbados, Greenland, Jamaica, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the U.S. Virgin Islands. It is found over open country, savanna, wooded slopes and humid forests.
The chimney swift's wintering grounds were only discovered in 1944, when bands from birds banded (ringed) in North America were recovered in Peru. An indigenous Peruvian had been wearing the bands as a necklace.
📌 Behavior
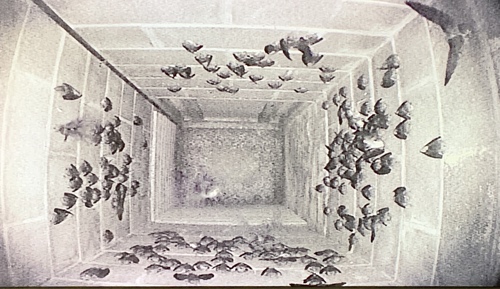
The chimney swift is a gregarious species, and is seldom seen alone. It generally hunts in groups of two or three, migrates in loose flocks of 6–20, and (once the breeding season is over) sleeps in huge communal roosts of hundreds or thousands of birds. Like all swifts, it is a superb aerialist, and only rarely seen at rest. It drinks on the wing, skimming the surface of the water with its beak. It also bathes on the wing, gliding above the surface of a body of water, briefly smacking its breast into the water, then flying off again, shaking its feathers as it goes. It has been recorded by pilots flying more than a mile above the surface of the earth, including one seen at . It is incapable of perching upright like most birds do; instead, it clings to vertical surfaces. If it is disturbed while at rest, the chimney swift will clap its wings loudly once or twice against its body; it does this either in place, or while dropping down several feet to a lower location. This behavior can result in a loud "thundering" sound if large roosts of the birds are disturbed. The sound is thought to be the bird's way of scaring away potential predators.
📌 Feeding
Like all swifts, the chimney swift forages on the wing. Studies have shown that of its food items are flying insects, including various species of flies, ants, wasps, bees, whiteflies, aphids, scale insects, stoneflies and mayflies. It also eats airborne spiders drifting on their threads. It is an important predator of pest species such as the red imported fire ant and the clover root curculio. Researchers estimate that a pair of adults provisioning a nest with three youngsters consume the weight equivalent of at least insects per day. Like many bird species, the chimney swift periodically coughs up pellets composed of indigestible bits of prey items.
During the breeding season, at least half of the chimney swift's forays occur within of its nest; however, it ranges up to away. While most of its food is seized following aerial pursuit, some is gleaned from the foliage of trees; the bird hovers near the ends of branches or drops through upper canopy levels. The chimney swift generally flies quite high, though it descends during cold or rainy weather. When feeding, it regularly occurs in small groups, and sometimes hunts with swallows, particularly barn swallows and purple martins; in mixed-species flocks, it is typically among the lower fliers. There is at least one record of a chimney swift attempting to steal a dragonfly from a purple martin, and it has been observed chasing other purple martins. In general, it is a diurnal feeder which remains active into early evening. However, there are records, particularly during migration periods, of chimney swifts feeding well after dark over brightly lit buildings.
The species shows two-weight peaks each year: one at the start of the breeding season, and a higher one shortly before it begins its migration south in the autumn. Its lowest weights are typically recorded during the breeding season, when it also begins a complete molt of its plumage. The chimney swift's weight gain before migration is smaller than that of some passerines, suggesting that it must refuel en route at various stopover points.
📌 Breeding
]]
The chimney swift is a monogamous breeder which normally mates for life, though a small percentage of birds change partners. Pairs perform display flights together, gliding with their wings upraised in a steep "V", and sometimes rocking from side to side. Breeding birds arrive as early as mid-March in the southern U.S., and late-April to mid-May in the Canadian provinces.
Before the arrival of European colonists into North America, the chimney swift nested in hollow trees; now, it uses human-built structures almost exclusively. While the occasional nest is still built in a hollow tree (or, exceptionally, in an abandoned woodpecker nest), most are now found inside chimneys, with smaller numbers in airshafts, the dark corners of lightly used buildings, cisterns, or wells. The nest is a shallow bracket made of sticks, which the birds gather in flight, breaking them off trees. The sticks are glued together (and the nest to a vertical surface) with copious amounts of the bird's saliva. During the breeding season, each adult's salivary glands more than double in size, from in the non-breeding season to during the breeding season.
Unlike some swift species, which mate in flight, chimney swifts mate while clinging to a vertical surface near their nest. They copulate daily, until the clutch is complete. The female typically lays , though clutch sizes range from . The eggs, which are long and elliptical in shape, are moderately glossy, smooth and white, and measure . Each weighs nearly of the female's body weight. Incubated by both parents, the eggs hatch after . Baby chimney swifts are altricial—naked, blind and helpless when they hatch. Fledglings leave the nest after a month.
The average chimney swift's life span is , but one is known to have lived more than . It was originally banded as an adult, and was recaptured in another banding operation some later.
📌 Predators and parasites
Mississippi kites, peregrine falcons and merlins are raptors that are known to take adult chimney swifts in flight, being among the select few avian hunters fast enough to overtake the appropriately named swift on the wing. When disturbed by potential predators (including humans) at the colony, adult chimney swifts slap their wings together after arching back and taking flight, making a very loud noise known either as "booming" or "thunder noises". When disturbed, nestlings make a loud, raspy raah, raah, raah sound. Both sounds seem designed to startle potential predators.
The chimney swift carries a number of internal and external parasites. It is the type host for the nematode species Aproctella nuda, the feather mite species Euchineustathia tricapitosetosa, and the biting lice species Dennyus dubius, and is also known to carry the tapeworm species Pseudochoanotaenia collocaliae. Its nest is known to host the Hemiptera species Cimexopsis nyctali, which is similar to the bed bug and can (on rare occasions) become a pest species in houses.
📌 Voice
The chimney swift has a twittering call, consisting of a rapid series of hard, high-pitched chirps. It sometimes gives single chirps.
📌 Conservation status
In 2010, the International Union for Conservation of Nature changed the chimney swift's status from least concern to near threatened. In 2018, the IUCN changed the chimney swift's status from near threatened to vulnerable. Although the global population is estimated at , it has declined precipitously across the majority of its range.
After sudden temperature drops, the chimney swift sometimes hunts low over concrete roads (presumably following insect prey drawn to the warmer road), where collisions with vehicles become more likely. More than 700 were found dead. The following year, roost counts in the province of Quebec, Canada, showed a decrease of 62 percent, and the overall population in the province was halved.
📌 History of observation
In 1899, Mary Day of New Jersey observed a pair of chimney swifts nesting in a chimney, and noted the incubation period was 19 days. The first detailed study of chimney swifts began in 1915 by self-taught ornithologist Althea Sherman in Iowa. She commissioned a 28 foot tall tower, of a similar design to a chimney, with ladders and peep holes installed to facilitate observation. Chimney swifts nested in her tower, and for over fifteen years, she meticulously recorded her observations, filling over 400 pages. Sherman remarked that although the tower had been designed with a limited knowledge of the nesting behavior of chimney swifts, after many years of observation she believed that the original design was ideal.